
Erosive tooth wear and gastro-oesophageal reflux, oral lichen planus and oro-facial manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus were popular blogs in April, May and June of 2020.
[read the full story...]
Erosive tooth wear and gastro-oesophageal reflux, oral lichen planus and oro-facial manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus were popular blogs in April, May and June of 2020.
[read the full story...]
This review of the effects of dietary acids and habits on dental erosion in the permanent dentition of 10- to 19-year-old adolescents included 52 observational studies. While the findings suggest some risk factors may contribute to dental erosion more high quality prospective studies are needed.
[read the full story...]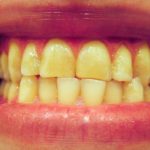
This review of diagnostic tools for sleep bruxism included 8 studies the majority being at high risk of bias. Portable diagnostic devices had best validity but quality of evidence was very-low to moderate.
[read the full story...]
This cohort study followed 13-14 year old Swedish adolescents over 4 years finding high incidence and prevalence of erosion, with higher levels being seen in males.
[read the full story...]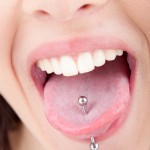
Twelve observational studies were included in this review which suggested that lip and tongue piercings increased the risk of gum and tooth damage . The relative risk for tooth damage with lip piercings was 1.33 (95%CI; 0.74 to 2.41) and 2.44 (95%CI;1.35 to 4.41) for tongue piercings.
[read the full story...]
Dental erosion is considered to be an increasing problem. However, clear information about the number of people affected is lacking. This review of 22 observational studies suggests that the worldwide prevalence is 30.4% (95%CI 23.8–37.0). However there is considerable heterogeneity between the studies in part related to the number of indices currently being used to measure tooth wear. So the estimate needs to be viewed with caution.
[read the full story...]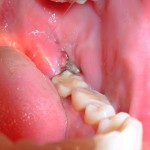
It has been estimated that about 25% of 10-40 year old European adults were affected by tooth wear (See Dental Elf 30th Sept 2013). The aim of this review was to identify similarities among treatment options for generalized tooth wear and to develop an approach to rehabilitation based on the best evidence available. Searches were [read the full story…]

Public Health England has just launched the third edition of the evidence-based toolkit for prevention. The first edition was published in 2007 and is considered to have been important in ensuring consistency of advice delivered as part of preventive treatment plans. Within England it has also helped inform commissioners develop dental contracts that encourage prevention. [read the full story…]
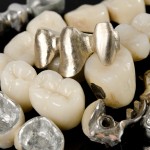
Some degree of tooth wear is a result of normal tooth-to-tooth contact. Some restorations have different wear characteristics and have been shown to produce accelerated wear. The aim of this review was to assess tooth wear against ceramic crowns in posterior region both in vitro and in vivo. Searching was restricted to the Medline database. [read the full story…]

There is increasing interest in the levels of tooth wear being seen with a recent systematic review suggesting that between 10-30% of children have signs of established wear ( Dental Elf Sept 2011) . The aim of this study was to determine prevalence of tooth wear on the oral and facial surfaces in 18– 35 year [read the full story…]