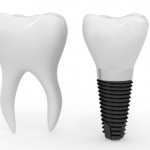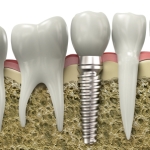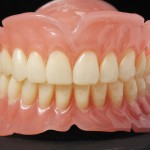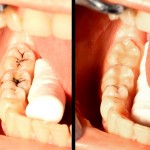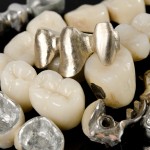
Crowning of teeth has been carried out for many years in order to replace damaged/diseased tooth structure or to improve aesthetics. Increasing patient demand has helped lead developments in ceramic technology and zirconium is one of the new materials in this field. The aim of this study was to compare the clinical survival rates of [read the full story…]