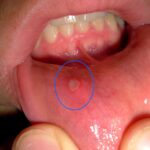
This review of different topical medications for the management of recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS) included 43 RCTs. No significant differences were found for any if the treatments assessed and a majority of the included RCTs (76%) were considered to be at high risk of bias.
[read the full story...]