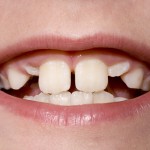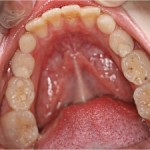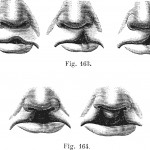
Cleft lip and palate is a relatively common birth defect that occurs in around 1 in 700 births and there have been contradictory reports of caries prevalence in CLP populations with some studies finding no difference and others an increase in prevalence. The aim of this review was to evaluate caries prevalence in non-syndromic patient [read the full story…]