
This review comparing articaine and lidocaine for local anesthesia use in children only identified 6 low quality studies. Little difference was seen between the two agents.
[read the full story...]
This review comparing articaine and lidocaine for local anesthesia use in children only identified 6 low quality studies. Little difference was seen between the two agents.
[read the full story...]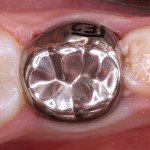
3 caries management options [conventional restorations (CR), the hall technique (HT), and non-restorative caries treatment (NRCT)] were investigated in this RCT. A 93% success rate was seen for the HT at 2.5 years compares with 70% for NRCT and 67% for CR.
[read the full story...]
This review of the local or systemic signs and symptoms during the eruption of the primary teeth included 16 observational studies only 5 of which were at low risk of bias. The overall prevalence of signs and symptoms associated with primary tooth eruption in children between 0 and 36 months was 70.5% (95%CI; 54.1-84.6).
[read the full story...]
20 studies were identified for this review of oral health related quality of life in children following general anaesthetic (GA). While a majority demonstrated an improvement following GA most are based on convenience samples and are of limited quality so more high quality research is needed.
[read the full story...]
This review of silver diamine fluoride (SDF) to arrest caries included 19 studies and suggest that 38% SDF can arrest 81% ( 68-89%) of active caries. . However none of the available studies was at low risk of bias so the findings should be interpreted cautiously.
[read the full story...]
The Hall technique is a relatively new management technique for caries in primary molars. This trial compares it use against the conventional approach and a non-restorative approach. Results at one year suggest that the Hall technique performed best.
[read the full story...]
The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare two different white MTA cements as pulpotomy medicaments in human primary teeth, Pro-Root MTA and MTA Angelus. Child patients with deep occlusal carious lesion, which presented potential risk of pulp exposure during complete removal of carious dentin, as determined by clinical and radiographic assessment were [read the full story…]

When I was training formocresol was the standard dressing for primary teeth following pulpotomy . However, it use is now questionable because of potential adverse effects such as potential carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, and cytotoxicity. Consequently a range of other materials have been investigated, ferric sulphate, gluatraldehyde preparations , mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), electrosurgery, calcium hydroxide, and laser [read the full story…]
The aim of this study was to compare the use of ferric sulphate (FS), formocresol (FC), mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) as pulp dressing following pulpotomy in primary molars. Symptom-free vital primary molars with carious pulp exposure with the possibility of proper restoration of the teeth with a minimum of three walls [read the full story…]
Pulpotomy procedure are used to maintain a carious tooth by removing the infected pulp and lasers have been shown to reduce bacterial levels in human tissue. The aim of this review was to identify studies comparing laser with conventional techniques for pulpotomy procedures in primary teeth and to evaluate their methodological quality, to assess whether [read the full story…]