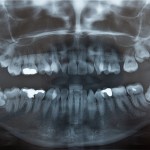
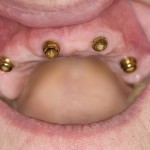
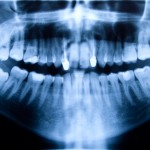
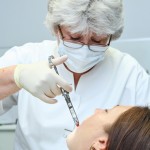
Grafting to augment the floor of the maxillary sinus prior to placement of dental implants in the resorbed maxillary is an increasingly used technique. The aim of this review was to evaluate the effects of smoking on the survival rate of dental implants placed in areas of maxillary sinus floor augmentation. Searches were conducted in [read the full story…]