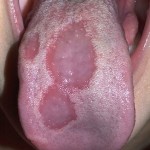
Lichen planus (LP) is an inflammatory condition that affects the skin and the squamous epithelium of mucosal surfaces lining the mouth, ears, eyes, and nose as well as the gastrointestinal and anogenital tracts. Two main patterns of inflammation are described: the plaque (raised) type and the erosive (raw) type, although bullous, blistering, or hypertrophic (thickened)types [read the full story…]