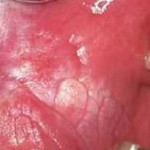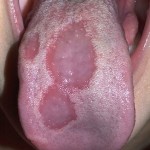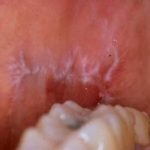
This review comparing low level laser therapy (LLLT) with steroids for the treatment of oral lichen planus only identified 5 studies none of which were at low risk of bias. Further high quality trials are needed to assess the efficacy of LLLT.
[read the full story...]