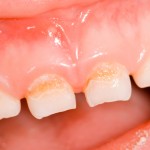
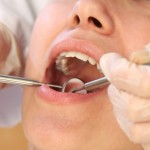
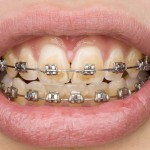
This review of the efficacy of mouthwashes on oral microorganisms and gingivitis in orthodontic patients included 32 RCTs. While the findings suggest short-term benefits with adjunctive mouthwash use the findings should be intertpreted cautiously as only one RCT was at low risk of bias and for almost all outccomes the certainty of evidence was rated as very low to low.
[read the full story...]