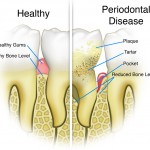
This review of adjuvant antibiotics for diabetics undergoing periodontal treatment included 13 small RCTs. While a statistically significant improvement in probing depth was seen the magnitude of this improvement is unlikely to be clinically significant.
[read the full story...]