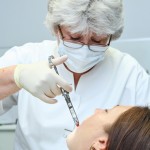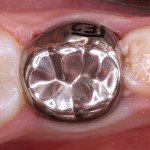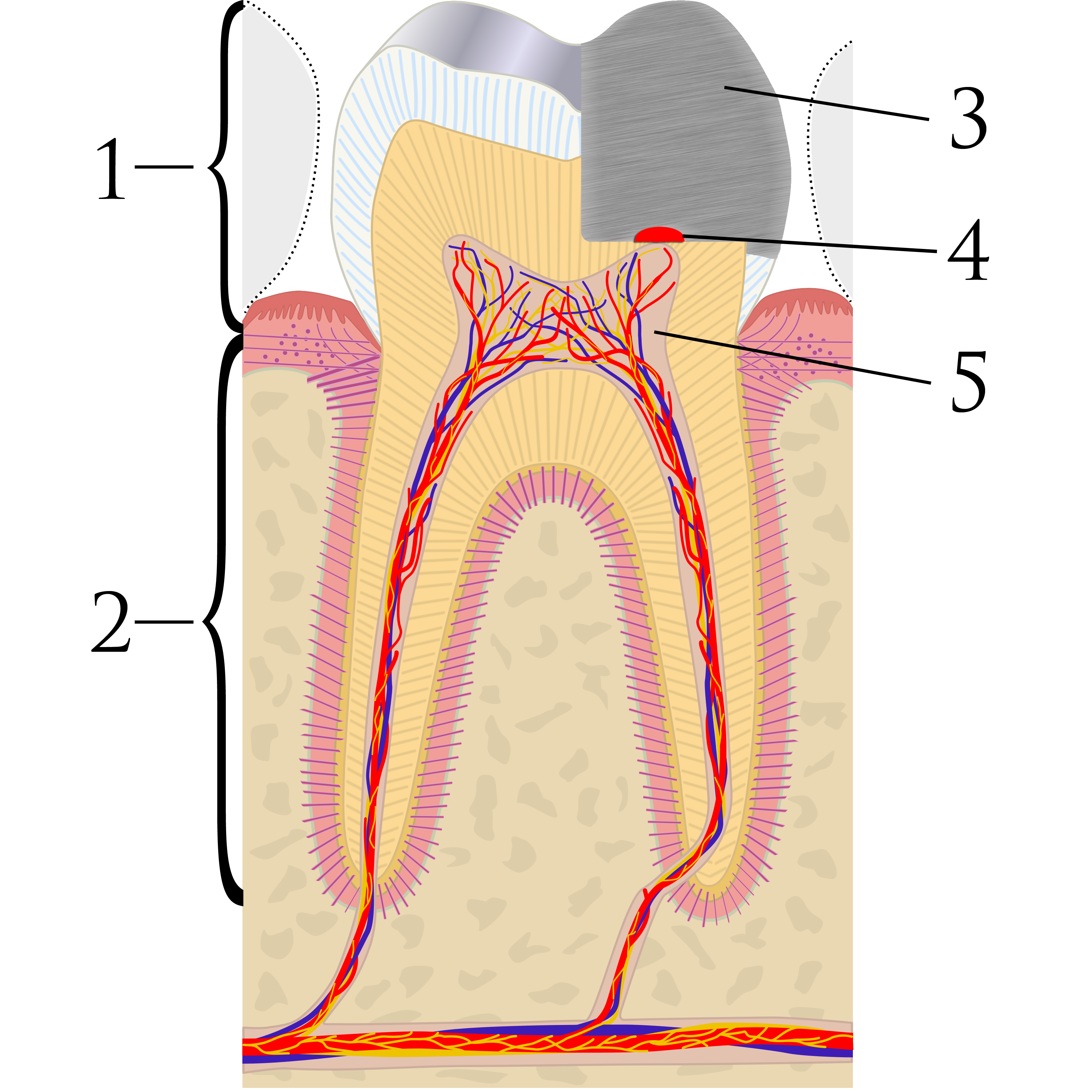
This review of the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of pulpotomy and associated medicaments in permanent teeth with pulp exposure included 17 RCTs some os which are still ongoing. The findings suggest that pulpotomy may be a potential treatment option for permanent teeth but more research is needed.
[read the full story...]