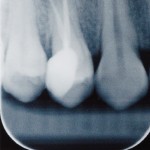
This network meta-analysis of oral premedication to improve anaesthetic success of inferior alveolar nerve block in patients with irreversible pulpitis suggest that that oral premedication with dexamethasone, NSAIDs and Tramadol increases the success rate.
[read the full story...]