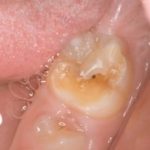
This review of adverse health conditions in the prenatal, perinatal and postnatal periods and associations with hypomineralised second primary molars(HSPM) included 14 studies. The findings suggest associations between HSPM and a number of condition but findings should be interpreted cautiously.
[read the full story...]