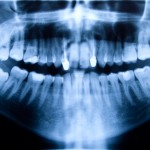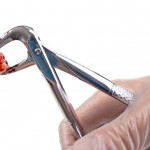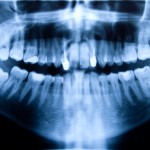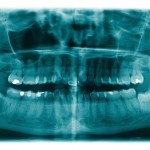
This review of antibiotic prophylaxis for the removal of third molars included 22 RCTs and suggest that antibiotic use lowered the infection risk by 60%. The number pf patients needed to treat to prevent one infection was 14 (95%CI;11-19).
[read the full story...]