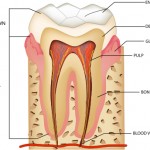
While Computed Tomography (CT) is a well-established diagnostic tool in many areas of medicine it is only since the development of Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) that is use in dentistry is beginning to be explored. 2012 saw the publication of new European evidence-based guidelines on CBCT for dental and maxillofacial radiology as a result [read the full story…]