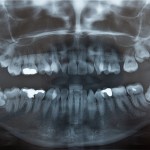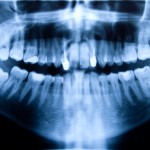
Dry socket (alveolar osteitis) socket is a painful complication of tooth extraction that occurs in about 5% of extractions of permanent tooth. It is more common following the extraction of wisdom teeth. That aim of this review was to assess whether chlorhexidine, when compared to placebo and/or other interventions, reduced the incidence of alveolar osteitis [read the full story…]