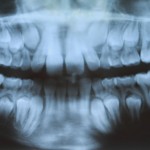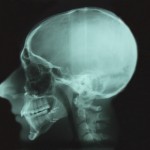
Lateral cephalometric radiographs were introduced in the 1930s and together with their related analysis have been a standard element of orthodontic treatment planning. However their role in assessment and treatment planning has been questioned. The aims of this review were to evaluate the existing evidence about the validation of lateral cephalometric radiograph in orthodontics and [read the full story…]