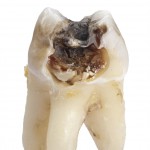
The use of topical fluoride together with fluoridated water and fissure sealants are mainstays of caries management. A range of non-fluoride agents caries preventive agents are also in use and these are reviewed to provide evidence-based clinical recommendations. The authors evaluated studies of sucrose-free polyol chewing gums, xylitol dentifrices, chlorhexidine, chlorhexidine in combination with thymol, [read the full story…]