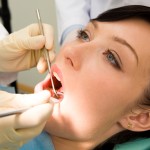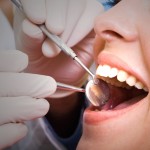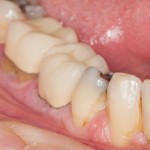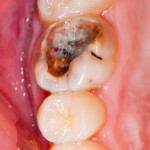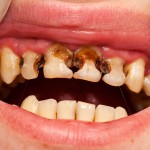
This review is part of the 2010 Global Burden of Disease study. It included a large number of observational studies and estimates that 2.4 Billion have untreated decay in permanent teeth and 621 million children have untreated caries in primary teeth.
[read the full story...]