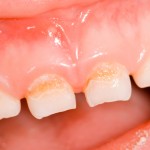
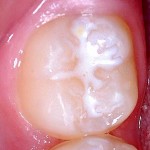
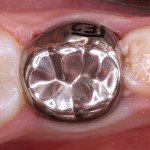
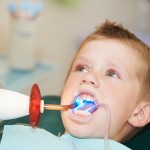
Data from a cohort of children (6-11 years old) participating in the Canadian Health Measures Survey (CHMS) suggests an association between vitamin D status and dental caries. Children with 25(OH)D concentrations ≥75 nmol/L had a 39% lower odds of having experienced caries.
[read the full story...]