Study suggests that single application of prophylaxis paste can reduce dentine hypersensitivity
Dentine hypersensitivity (DH) is a relatively common problem and we have reported on a number of studies and reviews over the past 12 months that have assessed various treatments to alleviate this problem. This aim of this study was to determine the effectiveness of a prophylaxis paste containing 15% calcium sodium phosphosilicate (NovaMin® ), with [read the full story…]
Study shows that tooth wear was present in around 30% of young European adults
There is increasing interest in the levels of tooth wear being seen with a recent systematic review suggesting that between 10-30% of children have signs of established wear ( Dental Elf Sept 2011) . The aim of this study was to determine prevalence of tooth wear on the oral and facial surfaces in 18– 35 year [read the full story…]
Trial suggests that root canal treatments with and without additional ultrasonic activation of the irrigant are equally effective
Irrigation procedures and protocols are a key stage in root canal therapy. The aim of this study was to compare the effectiveness of root canal treatments with and without additional ultrasonic activation of the irrigant by evaluating the endodontic outcome. Patients with a single-rooted maxillary or mandibular incisor, canine, or premolar tooth the required root [read the full story…]
Study suggests that text reminders may improve oral hygiene compliance during orthodontic treatment
Compliance with oral hygiene measures during orthodontic treatment is important in order to prevent white spot lesions (WSL) developing. The aim of this study was to determine if there is a relationship between reminding patients of the importance of oral hygiene via weekly text message reminders sent to their parents/guardians and demonstrated oral hygiene compliance. [read the full story…]
Review suggests that counselling may have a role in management of temporomandibular disorders

Temporomandibular disorders (TMD) are a group of disorders with symptoms that include pain, clicking, grating in the jaw joint and/or problems chewing or opening the jaw. It has been estimated that around 75% of the population have at least one sign of TMD. The aim of this review was to assess the effectiveness of counselling [read the full story…]
Barriers experienced by dentists in delivering care to older people

An increase in the proportion of older people in the population is evidence, with those aged 65 years of age and above expected to increase from 19 to 25 % in Europe by 2025. Coupled with an improvement in oral health over the past 30 years this means a higher proportion of these older people [read the full story…]
Does vomer or palatal flap have less adverse effect on maxillary growth in cleft patients? – No good evidence available
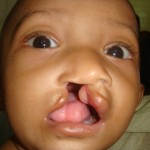
Cleft lip (CL) and cleft palate (CP) are common birth defects that affect around 1 in 700 children born. Surgery to repair the palate is thought to affect maxillary growth. The vomer flap is assumed to cause less scarring and therefore have less impact on growth. The aim of this review was to investigate the [read the full story…]
Oral cancer support needs are highly subjective and varied in severity across the cancer continuum

Worldwide oral and oropharyngeal cancer is the 6th most common cancer. Treatment often affects the individuals’ ability to eat, speak and interact with others and so is associated with significant physical and psychological burdens. This review aimed to describe the quality of life (QoL) outcomes and support needs in patients with oral cancer along the [read the full story…]
No randomised controlled trial evidence on effective methods to treat relapse of lower front teeth following orthodontic treatment

The tendency for teeth to return to their pre-treatment following orthodontic treatment (relapse) is more common for the lower front teeth. Ten years after orthodontic treatment between 30-50% of patients no longer have the initial post-treatment alignment and after 20 years only 10% maintain that alignment. The aim of this review was to assess the [read the full story…]
Only poor quality evidence available for the use of fluoride and calcium to prevent dental erosion
Dental erosion can been defined as the irreversible loss of tooth tissue by chemical processes not involving bacteria. The incidence of dental erosion is considered to be on the increase. The aim of this review was to assess the effectiveness of calcium and fluoride in the prevention of dental erosion. The PubMed, Cochrane Database of [read the full story…]
