Use of buffered lidocaine did not provide better pain control than unbuffered lidocaine for incision and drainage procedures

A 2010 Cochrane review (Cepeda et al) found that there was less pain associated with pain on injection and augmented patient comfort and satisfaction with the use of buffered lidocaine compared with unbuffered lidocaine in both parallel and crossover trials. Although none of the 23 trials included in the review were dental. The aim of [read the full story…]
Only poor quality evidence available to assess the effect of probiotics on caries

The use of probiotics for a wide range of conditions has been promoted and a potential caries protective effect has also been postulated. The aim of this review was to assess the caries preventive effect of probiotics in humans. The Medline and Embase databases were searched for randomised controlled trials assessing the in vivo role [read the full story…]
Trial shows similar survival for direct and indirect resin composite restoration of fractured cusps
Cusp fractures of restored posterior teeth are a frequent occurrence with the majority being reported as being supra gingival. While crowing the tooth is a conventional treatment approach it does require removal of substantial tooth substance. Adhesive restorations are a potential alternative approach and can be undertaken using direct or indirect approaches. The aim of [read the full story…]
ADA updates its clinical recommendations on topical fluoride for caries prevention
In 2006 the American Dental Association (ADA) published recommendations regarding professionally applied topical fluorides. An update of these guidelines has just been published. An executive summary is available from the Journal of the American Dental Association and the full report can be downloaded from the ADA – Centre for Evidence-based Dentistry (ADA-EBD) website (see links). [read the full story…]
Review reiterates that certain features of dental neglect are clearly identifiable
Sadly child mistreatment, including abuse and neglect are a reality in society. In the UK, dental neglect has been defined as, ‘‘the persistent failure to meet a child’s basic oral health needs, likely to result in the serious impairment of a child’s oral or general health and development’’. The aim of this review was to identify [read the full story…]
Little evidence to assess the effect of ceramic crowns on natural tooth wear
Some degree of tooth wear is a result of normal tooth-to-tooth contact. Some restorations have different wear characteristics and have been shown to produce accelerated wear. The aim of this review was to assess tooth wear against ceramic crowns in posterior region both in vitro and in vivo. Searching was restricted to the Medline database. [read the full story…]
Review suggests cleft lip and or palate patients may have higher prevalence of caries
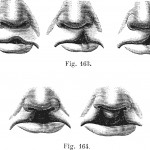
Cleft lip and palate is a relatively common birth defect that occurs in around 1 in 700 births and there have been contradictory reports of caries prevalence in CLP populations with some studies finding no difference and others an increase in prevalence. The aim of this review was to evaluate caries prevalence in non-syndromic patient [read the full story…]
Review suggests that radiotherapy was associated with higher rates of implant loss

Implant–supported restorations show good success rates in healthy tissues while studies in irradiated jaws contrasting outcomes have been reported. The aim of this review was to assess the survival rate of titanium implants placed in irradiated jaws. The Medline, Embase, and CENTRAL, and OpenGRAY databases were searched together with a number of journals (Clinical Implant [read the full story…]
Review suggests that intraoral appliances are more effective than headgear in distalising upper first molars

Moving the upper molars backwards during orthodontic treatment is sometimes necessary. Appliances used for this are categorized in to intraoral or extraoral appliances. External headgear is one of the commonest distalising approaches. The aim of this Cochrane review was to assess the effects of orthodontic treatment for distalising upper first molars in children and adolescents. [read the full story…]

