Some evidence of reduction of peri-implant bone loss with platform switching

The concept and use of platform switching has gathered pace with the increasing numbers of dental implants being placed. platform switching (PS), where a small diameter implant abutment is placed in order to place the implant- abutment interface medial to the edge of the implant platform is considered to have a positive impact on maintaining [read the full story…]
Currently little evidence to support smoking as a risk factor for peri-implantitis

Dental Implants are now seen as a predictable treatment strategy for restoration in the partially or totally edentulous patient. Peri-implantitis is one potential complication and the prevalence has been reported as ranging from 6 – 28%. Smoking has been identified as a potential risk factor. The aim of this review was to assess the evidence [read the full story…]
Limited weak evidence suggesting that flapless dental implant placement is feasible
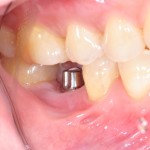
The use of dental implants is becoming an increasingly common procedure. Traditionally they have been placed after a mucoperiosteal flap has been raised. The concept of implants placement without raising a flap (flapless surgery) has been advocated as a way of achieving a shorter treatment time. The aim of this review was to evaluate the [read the full story…]
On-demand analgesic use following root canal treatment resulted in similar pain relief but reduced consumption compared with regular prescription
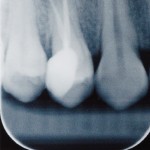
The management of pre- and post-operative pain is a key component of endodontic treatment with studies reporting that the incidence of post operative pain (flare-up) ranges from 3-58%. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the most common medication used for managing pain after root canal treatment (RoCT). The aim of this study was to compare the [read the full story…]
New Cochrane Protocols January 2014

Two more protocols for reviews are now available on the Cochrane Library The first one is:- El-Angbawi A, McIntyre GT, Bearn DR, Fleming PS. Non-surgical adjunctive interventions for accelerating tooth movement in patients undergoing fixed orthodontic treatment (Protocol). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 12. Art. No.: CD010887. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010887. The aim is to [read the full story…]
Moderate evidence that fluoride varnish applied regularly during orthodontic visits reduces enamel demineralisation
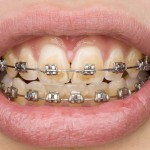
The development of early, but reversible, carious lesions or demineralised white lesions (DWLs) is one adverse effect of fixed appliance orthodontic treatment. The prevalence has been reported to be as high 70%, and although the majority are minor and fade with time as they resolve about 10% cavity and may require filings. The main aim [read the full story…]
No evidence to support or refute the practice of six-monthly dental check-ups

Having your teeth regularly examined by a dentist seems to have been recommended back as far the 18th Century (Richards 2002) and subsequently the six-monthly visit became de rigueur. The scientific basic for this interval was challenged by Sheiham in 1977 and there has subsequently been much debate about the clinical and cost-effectiveness of recall [read the full story…]
Positive association between alcohol drinking and upper aerodigestive tract cancers

Mouth cancers form part of a wider group of upper aerodigestive tract (UADT) cancers (oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, and oesphagus), which are strongly associated with smoking and alcohol. The aim of this review was to quantify the association between alcohol drinking and UADT cancer mortality The Medline and ISI Web of Science databases were searched [read the full story…]
Review suggests that smoking may have a harmful effect on peri-implant bone loss

It is believed that a number of factors may affect peri-implant bone resorption. These may include local factors (e.g. surgical procedures, implant design and restorative procedures), or patient related factors such as systematic disease, smoking status etc. The aim of this review was to determine the influence of patient-related systemic risk factors (systemic disease, genetic [read the full story…]
Ibuprofen more effective than paracetamol for postoperative pain following third molar removal
Surgical removal of third molars is a very common procedure and postoperative pain is a major concern for patients. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are (NSAIDs) frequently recommended to manage this pain. Ibuprofen and paracetamol commonly used and recently a combination analgesic containing both paracetamol and ibuprofen has become available in the UK. The aim of this [read the full story…]
